We are going to look at futures trading currencies. We will follow
information from Investopedia, an Internet site devoted to investing
education based in Edmonton in Alberta, Canada.
The spot foreign exchange (forex or FX) market is the world's largest
market, with over US$1 trillion traded per day. One derivative of this
market is the forex futures market, which is only one one-hundredth the
size. This article examines the key differences between forex futures and
hedging with this useful derivative.
SEE: Forex Tutorial
Forex Futures Vs. Traditional Futures
Both forex and traditional futures operate in the same basic manner:
a contract is purchased to buy or sell a specific amount of an asset
at a particular price on a predetermined date. There is, however, one
key difference between the two: forex futures are not traded on a centralized
exchange; rather, the deal flow is available through several different
exchanges in the United States and abroad. The vast majority of forex futures
partners (introducing brokers).
However, this is not to say that forex futures contracts are
It is important to remember that all currency futures quotes are made against the
U.S. dollar, unlike the spot forex market.
SEE: Futures Fundamentals
Here is an example of what a forex futures quote looks like:
Here is an example of what a forex futures quote looks like:
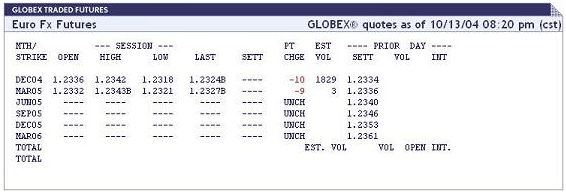
Euro FX Futures on the CME For any given futures contract, your broker should provide you with its specifications,
such as the contract sizes, time increments, trading hours, pricing limits and other
relevant information. Here is an example of what a specification sheet might look like:
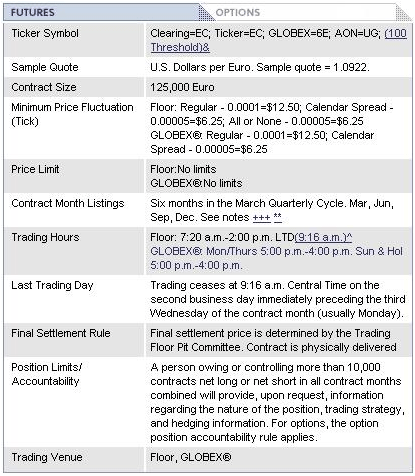 |
| Figure 2: Specification Sheet from CME. |
Hedging Vs. Speculating
Hedging and speculating are the two primary ways in which forex derivatives are
used. Hedgers use forex futures to reduce or eliminate risk by insulating themselves
against any future price movements. Speculators, on the other hand, want to incur
risk in order to make a profit. Now, let's take a more in-depth look at these two
strategies.
Hedging
There are many reasons to use a hedging strategy in the forex futures market. One
main purpose is to neutralize the effect of currency fluctuations on sales revenue.
For example, if a business operating overseas wanted to know exactly how much
revenue it will obtain (in U.S. dollars) from its European stores, it could purchase a
futures contract in the amount of its projected net sales to eliminate currency
fluctuations.
SEE: Spotting A Forex Scam
When hedging, traders must often choose between futures and another derivative
When hedging, traders must often choose between futures and another derivative
known as a forward. There are several differences between these two instruments,
the most notable of which are these:
• Forwards allow the trader more flexibility in choosing contract sizes and setting dates.
• Forwards allow the trader more flexibility in choosing contract sizes and setting dates.
This allows you to tailor the contracts to your needs instead of using a set contract
size (futures).
• The cash that's backing a forward is not due until the expiration of the contract,
whereas the cash behind futures is calculated daily, and the buyer and seller are
held liable for daily cash settlements. By using futures, you have the ability to
re-evaluate your position as often as you like. With forwards, you must wait until the
contract expires.
SEE: Forex Walkthrough
Speculating
Speculating is by nature profit-driven. In the forex market, futures and spot forex
are not all that different. So why exactly would you want to participate in the futures
market instead of the spot market? Well, there are several arguments for and
against trading in the futures market:
Advantages
• Lower spreads (two to three).
• Lower transaction costs (as low as $5 per contract).
• More leverage (often $500+ per contract).
Disadvantages
• Often requires a higher amount of capital ($100,000 lots).
• Limited to the exchange's session times.
• National Futures Association fees may apply.
The strategies employed for speculating are similar to those used in spot markets.
The most widely used strategies are based on common forms of technical chart
analysis since these markets tend to trend well. These include Fibonacci studies,
Gannstudies, pivot points and other similar techniques. Alternately, some speculators
use more advanced strategies, such as arbitrage.
The Bottom Line
As we can see, forex futures operate similarly to traditional stock and commodity
futures. There are many advantages to using forex futures for hedging as well as
speculating. The distinguishing feature is that the futures are not traded on a
centralized exchange. Forex futures can be used to hedge against currency
fluctuations, but some traders use these instruments in pursuit of profit, just as
they would use futures on the spot market.
$4.95 Stock Trades with TradeKing
TradeKing offers great pricing - stock trades are only $4.95/trade! Plus, their licensed
brokers pride themselves on providing great service, short hold times, fast email
Follow us: @Investopedia on Twitter

No comments:
Post a Comment